主要代码流程图:

第1步:加载并启动ApplicationContext
1.1 概述
ApplicationContext顾名思义就是应用程序上下文的意思,作为整个应用程序的上下文,那么就应该包含应用程序主要功能,如bean创建、读取配置、消息国际化等。
源码中的注释是这样写的:Central interface to provide configuration for an application.This is read-only while the application is running, but may bereloaded if the implementation supports this。
Spring项目在启动的时候,会根据不同项目的需求,应用到一个ApplicationContext:
- 如果是springboot的SpringApplication.run方式来启动,则会更具项目的配置自动选用AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(基于注解配置的servlet项目)、AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext(基于注解配置的webflux项目)或AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(基于注解配置的项目)
- 项目也可以直接用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(XXX.class)这种方式来启动(基于注解配置的项目)
- 项目也可以直接用XmlWebApplicationContext(XXX.class)这种方式来启动(基于xml配置的项目)
不同ApplicationContext的读取配置、创建bean的方式可能有些差异,但是总的流程都是差不多的。
ApplicationContext的主要功能:
- 应该能够具备应用程序Bean的创建能力,因此ApplicationContext实现了BeanFactory接口
- 应该能够获取应用程序的环境配置信息,因此ApplicationContext实现了EnvironmentCapable接口,通过EnvironmentCapable接口的getEnvironment可以获取应用程序的配置信息,如果getProperty、getActiveProfiles等
- 应该具备配置国际化消息的能力,因此实现了MessageSource接口
- 应该具备应用程序事件通知的能力,因此ApplicationContext实现了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,如ContextRefreshedEvent表示应用程序的上下文刷新完成事件、ApplicationStartedEvent表示应用程序启动完成事件、ApplicationReadyEvent表示应用程序准备好了事件、ContextClosedEvent表示应用程序的上下文关闭事件。(当然我们也可以通过ApplicationEventPublisher接口实现应用程序自定义的事件,对于分布式的应用建议用分布式的事件框架,不用spring的事件框架。spring的事件框架只在当前进程有效,因此适合单进程的App)
- 应该具备资源扫描能力,因此ApplicationContext实现了ResourcePatternResolver接口,如Application在启动的时候需要扫描ComponentScan定义的package下的所有类,如果ComponentScan没有定义,则会默认扫描App配置类所在packge下的所有class类资源
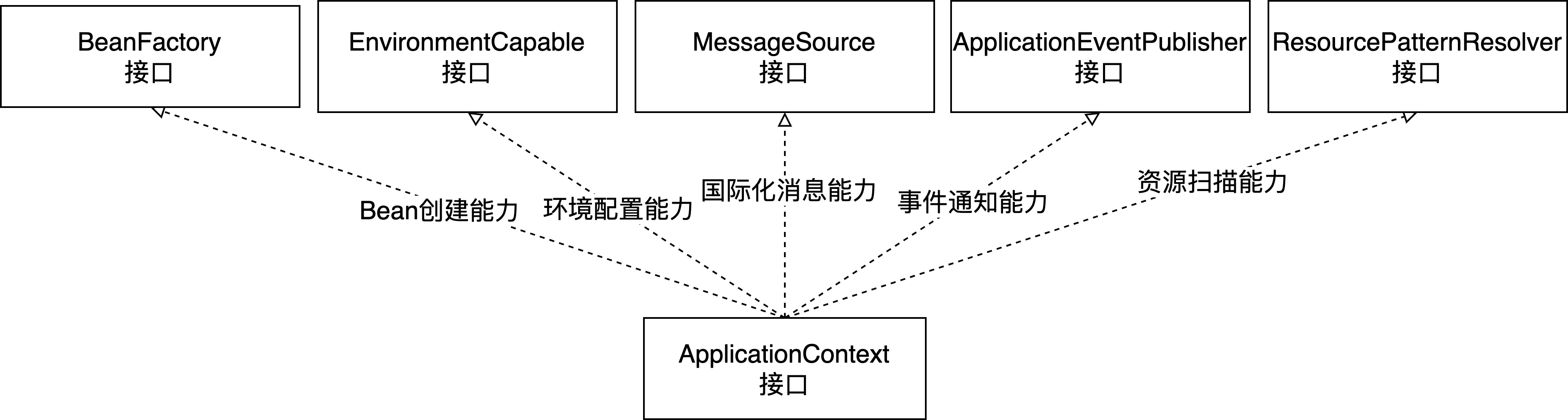
再回头来看看ApplicationContext类的定义可以印证:
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
1.2 springboot用到的三个主要的ApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext、AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext、和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
顾名思义,这三个ApplicationContext都是基于注解配置(AnnotationConfig)的ApplicationContext。SpringApplication在启动的时候会根据webApplicationType来创建不同的ApplicationContext,ApplicationContextFactory的代码片段如下图所示:
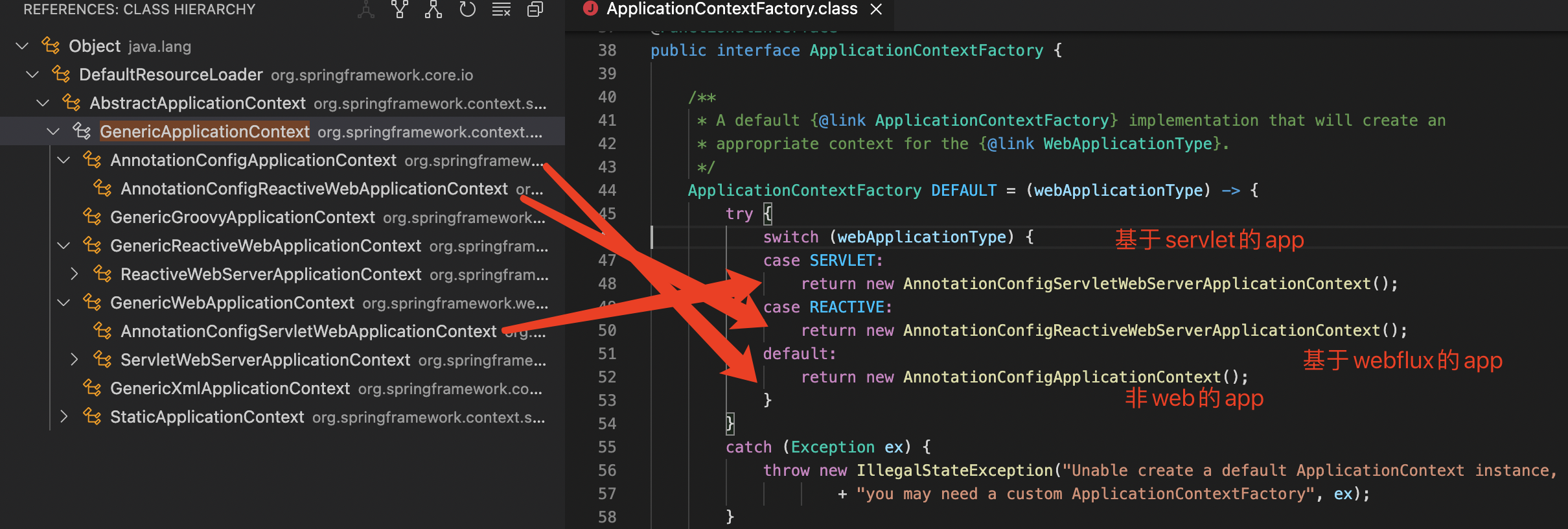
- 如果webApplicationType是SERVLET,则用AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 如果webApplicationType是REACTIVE,则用AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext,启用WebFlux框架
- 否则,则用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
Spring WebFlux 是 Spring Framework 5.0中引入的新的响应式web框架。与Spring MVC不同,它不需要Servlet API,是完全异步且非阻塞的,并且通过Reactor项目实现了Reactive Streams规范。
springboot的WebApplicationType类型配置:
-
我们的项目可以通过
application.yml中的spring.main.web-application-type来配置应用类型。 -
如果不配置,则根据以下代码逻辑决定应用类型:
public enum WebApplicationType {
// ConfigurableWebApplicationContext在spring-web-x.x.x.jar包中
// Servlet在tomcat-embed-core-x.x.x.jar或其它含servlet的jar包中
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
// DispatcherServlet在spring-webmvc-x.x.x.jar包中
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
// DispatcherHandler在spring-webflux-x.x.x.jar包中
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
// ServletContainer在jersey-container-servlet-core-x.x.jar包中
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
// 如果有spring-webflux的类,且无spring-webmvc,且无jersey-container的类
// 那么久是REACTIVE的web类型
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
// 如果没有spring-web的类,且没有servlet的类,则是NONE类型,即非web项目
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// 否则是SERVLET类型
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
...
通过以上代码,可以总结出以下规则:
- 如果项目引用了spring-boot-starter-webflux,没有引用spring-boot-starter-web和spring-boot-starter-jersey,则为REACTIVE类型
- 如果项目没有spring-web包和servlet相关的类,则项目默认为NONE类型
- 如果项目有spring-web包和servlet相关的类,则默认为SERVLET类型
通常情况下,我们的项目引用的是spring-boot-starter-web,因此默认就是SERVLET类型。
- 另外还可以通过以下方式设置WebApplicationType(不推荐)
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(xxx.class);
application.setWebApplicationType(WebApplicationType.xxx); //在这里设置WebApplicationType
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = application.run(args);
1.3 XmlWebApplicationContext
public class XmlWebApplicationContext extends AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext {
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION = "/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_PREFIX = "/WEB-INF/";
public static final String DEFAULT_CONFIG_LOCATION_SUFFIX = ".xml";
用SpringBoot后,XmlWebApplicationContext就很少使用了。以前的老的项目还有一些用XmlWebApplicationContext的,spring的默认配置放在/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,通过加载xml配置来启动spring。
1.4 ApplicationContext主要代码
- AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法:刷新应用程序的上下文,spring启动的主体流程可以通过这个方法看出来
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// 刷新前准备工作:创建environment并加载System.properties()及System.getenv()到environment中.
prepareRefresh();
// 创建BeanFactory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 为Bean工厂做准备,这里比较重要的就是整个了两个特殊的BeanPostProcessor
// 1. ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:
// 这个Processor用于执行Aware接口,如果我们写的Bean实现了如下Aware接口,将会执行该Aware接口的对应方法:
// EnvironmentAware、EmbeddedValueResolverAware、ResourceLoaderAware、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware、ApplicationContextAware
// 2. ApplicationListenerDetector
// 这个Processor是用于收集我们自己写的监听器,只要我们的Bean实现了ApplicationListener监听器,那么就会在初始化Bean期间调用postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法时被收集到这个Bean中,在调用postProcessAfterInitialization注册为Spring的监听器
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 扩展点,子类可以重写该方法,完成一些需要在BeanFactory创建后执行的操作
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// 执行上一步的扩展
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册上所有的BeanPostProcessors,所有BeanPostProcessor类型的Bean会在此时完成实例化
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// 国际化
initMessageSource();
// 初始化事件广播器,当事件发布器发布事件时,会调用这个广播器来广播事件.
// 广播器默认实现是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,这个监听器支持设置一个线程池来做异步处理
// 我们还可以设置errorHandler来统一处理所有监听事件的异常。前提是我们要自己定义一个BeanId为applicationEventMulticaster的ApplicationEventMulticaster
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 扩展点,子类可以重写该方法,完成一些定制的功能
onRefresh();
// 注册监听器,我们写的监听器也会在这里加上.
registerListeners();
// ∆∆∆∆实例化所有余下的非lazy-init的单利bean。(这一步是重点,我们定义的bean基本上都是在这一步实例化的)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 在所有Bean加载完毕后,在容器中找beanId为lifecycleProcessor的LifecycleProcessor,找到则用找到的,没有找到值创建一个默认的DefaultLifecycleProcessor,然后就会执行这个LifecycleProcessor的onRefresh方法。在DefaultLifecycleProcessor执行onRefresh方法时,会去容器中找SmartLifecycle类型的Bean,并执行SmartLifecycle.start()方法,可以在此处扩展整个BeanFactory创建及初始化完成后的操作.
// 发布一个ContextRefreshedEvent事件,SpringMVC就是基于这个事件扩展的
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
destroyBeans();
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
- AbstractApplicationContext的finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法:实例化bean的主要方法的入口
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// 调用beanFactory的实例化bean方法
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
第2步:通过BeanFactory创建bean
2.1 说明
顾名思义,BeanFactory是创建bean的工厂,它是IOC的主要接口,其中一个主要的子类就是AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
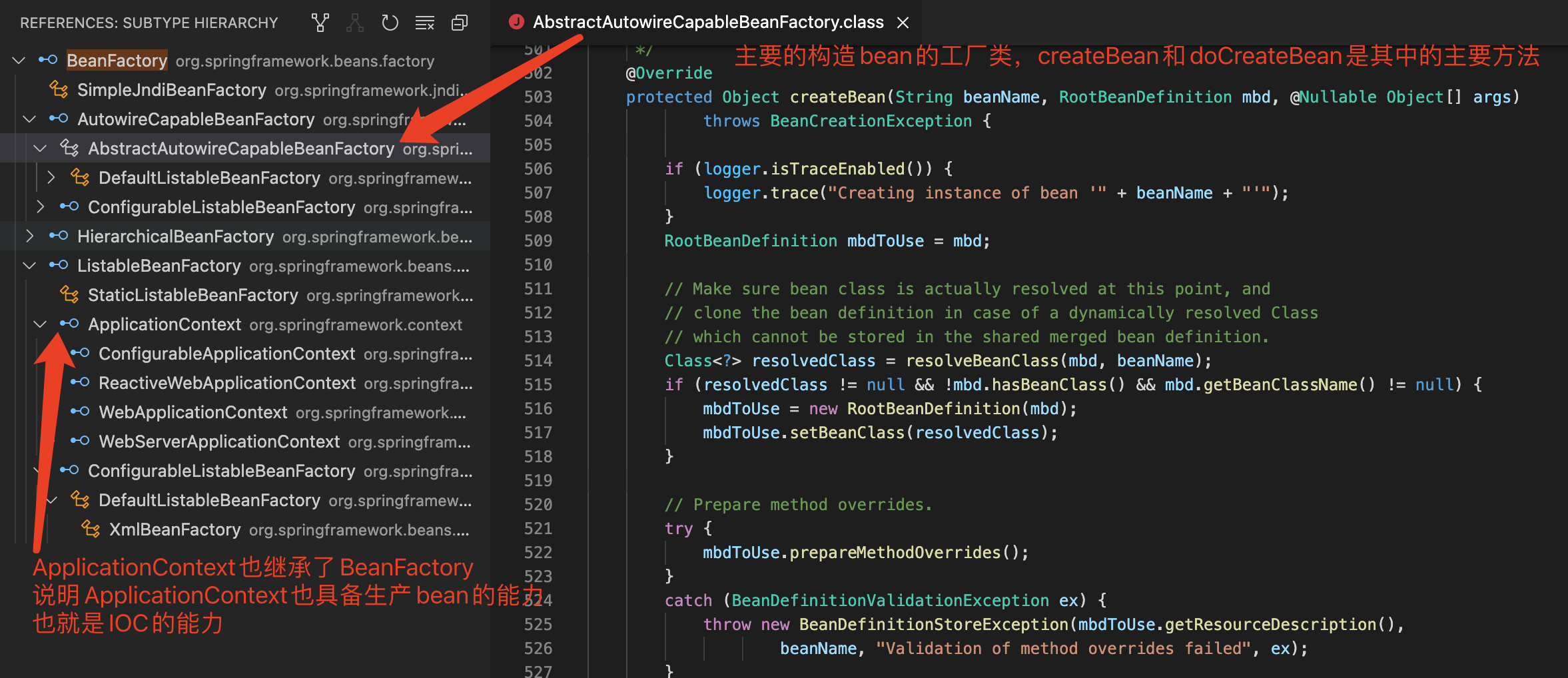
通过debug AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的代码,可以看出spring创建bean的主要流程如下图:
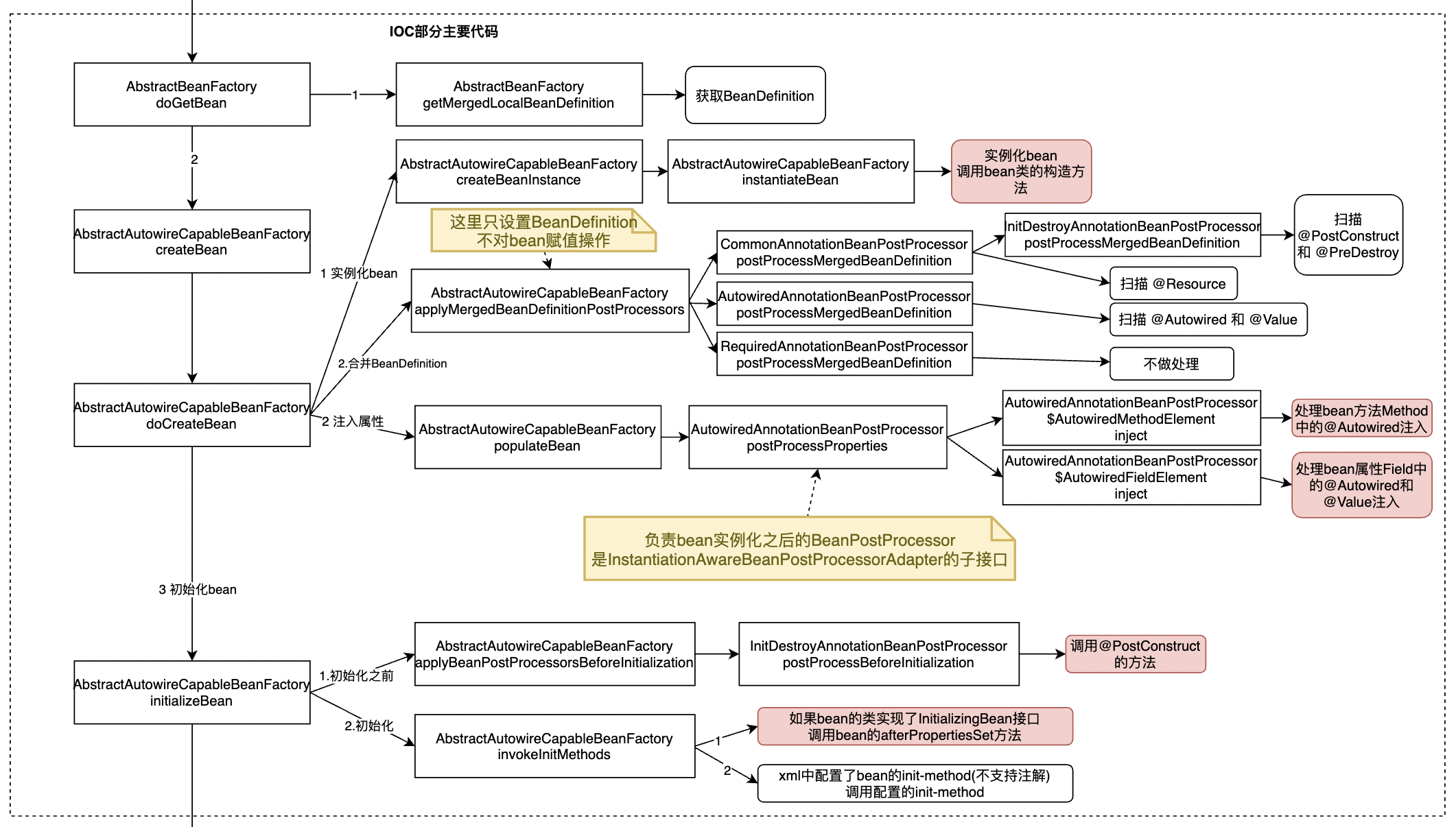
- AbstractBeanFactory类的getMergedLocalBeanDefinition方法:准备RootBeanDefinition,RootBeanDefinition中定义了Bean的所有配置信息
- 创建bean的实例,也就调用bean的构造方法
- 继续合并BeanDefinition,查找bean中配置的@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource、@Autowired 和 @Value等注解
- 处理bean方法Method中的@Autowired注入
- 处理bean属性Field中的@Autowired和@Value注入
- 调用@PostConstruct的方法
- 如果bean的类实现了InitializingBean接口,调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法
- xml中配置了bean的init-method(不支持注解),调用配置的init-method
- 创建bean之后,如果需要创建AOP代理,则通过AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator来创建AOP代理。
2.2 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory主要代码
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,顾名思义就是
具备自动化能力的Bean工厂类,不管是通过加载xml,还是基于注解来注入bean,都是用的这个抽象的自动化的bean工厂。
createBean调用了doCreateBean方法,主要的代码都在doCreateBean里面,doCreateBean的流程如下:
-
调用createBeanInstance方法创建bean实例,也就是调用bean类的构造方法
1.1调用instantiateBean方法
-
调用applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors方法,合并Beandefinition
2.1 调用CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,扫描@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource注解,将扫描信息设置到Beandefinition
2.2 调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,扫描@Autowired 和 @Value注解,将扫描信息设置到Beandefinition
2.3 调用RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessMergedBeanDefinition方法,改方法步做处理
-
调用populateBean方法,注入bean的属性值
3.1 调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的postProcessProperties方法
3.1.1 调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredMethodElement的inject方法,注入bean方法中@Autowired的值
3.1.2 调用AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$AutowiredFieldElement的inject方法,注入bean属性中@Autowired和@Value的值
-
调用initializeBean方法,初始化bean,调用bean的初始化方法
4.1 调用applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法,调用@PostConstruct的方法
4.2 调用invokeInitMethods方法;如果bean的类实现了InitializingBean接口,调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法;xml中配置了bean的init-method(不支持注解),调用配置的init-method
4.3 调用applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,做初始化之后的处理,比如创建AOP代理
4.3.1 调用AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的postProcessAfterInitialization方法,创建AOP代理
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建bean实例,也就是调用bean类的构造方法
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
// 合并Beandefinition,扫描@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource、@Autowired 和 @Value注解,将扫描信息设置到Beandefinition
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 注入bean的属性值;1.注入bean方法中@Autowired的值;2.注入bean属性中@Autowired和@Value的值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化bean,调用bean的初始化方法
// 1. 调用@PostConstruct的方法
// 2. 如果bean的类实现了InitializingBean接口,调用bean的afterPropertiesSet方法
// 3. xml中配置了bean的init-method(不支持注解),调用配置的init-method
// 4. 调用applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,做初始化之后的处理,比如创建AOP代理
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 中间代码省略
}
// 中间代码省略
return exposedObject;
}
2.3 BeanDefinition接口说明
BeanDefinition:定义了Bean的所有配置信息,IOC构造bean的时候基于BeanDefinition来构造
2.4 BeanPostProcessor接口说明
BeanPostProcessor:bean实例化之前和之后的处理器,包含了两个接口
postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,负责处理bean实例化之前的回调
postProcessAfterInitialization方法,负责处理bean实例化之后的回调
几个主要的BeanPostProcessor:
-
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类: 负责创建AOP代理
-
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口:负责合并BeanDefinition,包含的主要子类
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor负责扫描@PostConstruct @PreDestroy、和 @Resource注解
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor负责扫描@Autowired 和 @Value注解,它的AutowiredMethodElement子类负责处理bean方法Method中的@Autowired注入,子类负责处理bean属性Field中的@Autowired和@Value注入
2.5 解决bean循环依赖问题
通过三级缓存解决bean循环依赖问题。参考DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry类的getSingleton方法代码:
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
场景说明:
如果User依赖了Role,Role也依赖了User:
- 如果是构造方法循环依赖:死循环,只能改代码,无法解决,因为对象还没new出来
- 如果是set方法循环依赖:对象已经创建好,只是属性填充(DI)时遇到了循环依赖,spring能够解决
具体流程如下:
-
创建User对象
-
User对象实例化并将User对象的引用,提前暴露到三级缓存中,并且将User对象封装到一个ObjectFactory中
注意:objectFactory不克是可以获取User对象,还有可能是user对象产生的代理,也就是说返回的可能是原对象,也可能是代理工对象 三级缓存产生完对象之后,就会将产生出来的User对象(可能是原对象,也可能是代理对象)放入二级缓存
-
User对象依赖注入(setRole)
3.1 创建Role对象
3.2 Role对象实例化
3.3 依赖注入(setUser)
3.4 到二级缓存和三级缓存中去User对象
3.5 Role对象初始化
3.6 将Role对象放入一级缓存
-
User对象初始化
-
将User对象放入一级缓存
第3步:创建AOP代理
3.1 说明
创建AOP代码也是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean方法中完成的。
属于initializeBean方法的最后一步之流程
创建AOP代理是在Bean的构造以及所有属性、初始化都之心完成后开始的。
流程图如下:
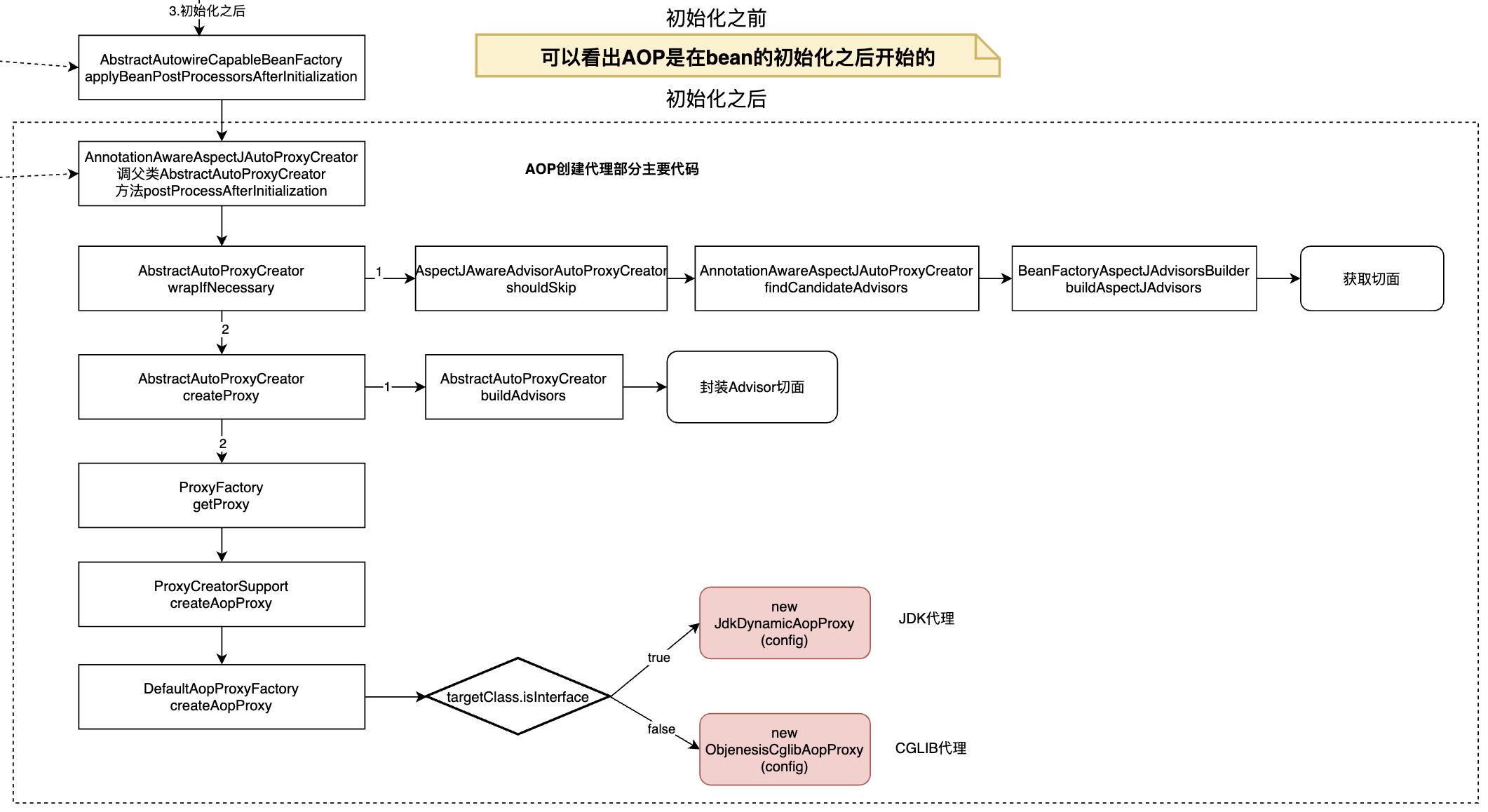
3.2 DefaultAopProxyFactory.createAopProxy代码
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() &&
(config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
// 创建JDK代理
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
// 创建CGLIB代理
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
3.3 主要概念
Join point(连接点):目标对象中的方法就是一个连接点,也就是aop拦截的具体的某一个方法。因为Spring只支持方法类型的连接点,所以在Spring中连接点指的就是被拦截到的方法,实际上连接点还可以是字段或者构造器。
Pointcut(切入点):用来定义怎么切入到连接点的,只是一个定义。比如@Pointcut("execution(* olivee.study.IWorker.work(..))")这个切点表示切入olivee.study.IWorker.work方法点执行
Advice(通知):AOP在特定的切入点上执行的增强处理,有before(前置),after(后置),afterReturning(最终),afterThrowing(异常),around(环绕)
Aspect(切面):包括切点pointcut,通知Advice的一个载体。在spring AOP中可以用一个注解了@Aspect的类来定义。
Target object(目标对象):原始对象,代理前的对象
AOP proxy(代理对象):代理后的对象
- Advice通知类型介绍
- Before:在目标方法被调用之前做增强处理,@Before只需要指定切入点表达式即可
- AfterReturning:在目标方法正常完成后做增强,@AfterReturning除了指定切入点表达式后,还可以指定一个返回值形参名returning,代表目标方法的返回值
- AfterThrowing:主要用来处理程序中未处理的异常,@AfterThrowing除了指定切入点表达式后,还可以指定一个throwing的返回值形参名,可以通过该形参名来访问目标方法中所抛出的异常对象
- After:在目标方法完成之后做增强,无论目标方法时候成功完成。@After可以指定一个切入点表达式
- Around:环绕通知,在目标方法完成前后做增强处理,环绕通知是最重要的通知类型,像事务,日志等都是环绕通知,注意编程中核心是一个ProceedingJoinPoint
图例:


3.4 AbstractAspectJAdvice的几个子类
- AspectJAfterAdvice:负责处理After通知
- AspectJAfterReturningAdvice:负责处理AfterReturning通知
- AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice:负责处理AfterThrowing通知
- AspectJAroundAdvice:负责处理Around通知
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice:负责处理Before通知
3.5 主要的类
- Interceptor:拦截器,Advice的子接口,标记拦截器。拦截器是增强器的一种。
- Methodinterceptor:方法拦截器,Interceptor的子接口,拦截方法并处理。
- Joinpoint:连接点。在拦截器中使用,封装了原方法调用的相关信息,如参数、原对象信息,以及直接调用原方法的proceed方法
- Invocation:Joinpoint的子类,添加了获取调用参数方法。
- Methodinvocation:Invocation的子类,包含了获取调用方法的方法。
- AbstractAspectJAdvice:负责处理通知的抽象类
- AspectJAfterAdvice:负责处理After通知
- AspectJAfterReturningAdvice:负责处理AfterReturning通知
- AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice:负责处理AfterThrowing通知
- AspectJAroundAdvice:负责处理Around通知
- AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice:负责处理Before通知